In resin-based 3D printing, FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) film plays a critical role in achieving accurate prints and prolonging printer lifespan.
Acting as a release layer between the resin vat and the UV light source, the thickness of PEP film directly impacts print quality, durability, and ease of removal. Choosing the right thickness can make the difference between flawless prints and frustrating failures.
This article compares common FEP film thicknesses and helps you determine which one works best for your 3D printer.
Why FEP Film Thickness Matters?
FEP film is known for its non-stick properties, optical clarity, and chemical resistance. However, its mechanical performance changes with thickness:
- Too thin: Easier resin release but reduced durability.
- Too thick: Longer lifespan but potential issues with print adhesion or light transmission.
The goal is to balance print quality, ease of use, and film longevity.
What Changes as the Thickness Varies?
1. Durability and Puncture Resistance
Thicker FEP film is mechanically stronger and resists pinholes and scratches longer.
2. Peeling Force
Resin printing involves peeling the cured layer from the FEP during each layer transition. Thinner FEP film usually flexes more easily, which lowers the suction and separation forces. Lower peel force:
- Reduces layer delamination and warping for tall, thin prints.
- Lowers stress on the Z-axis and build plate.
3. Optical Transmission and Accuracy
FEP film is highly transparent to UV wavelengths used in resin curing. Thinner FEP films offer slightly better light transmission and less scattering, which can marginally improve exposure efficiency and sharpness.
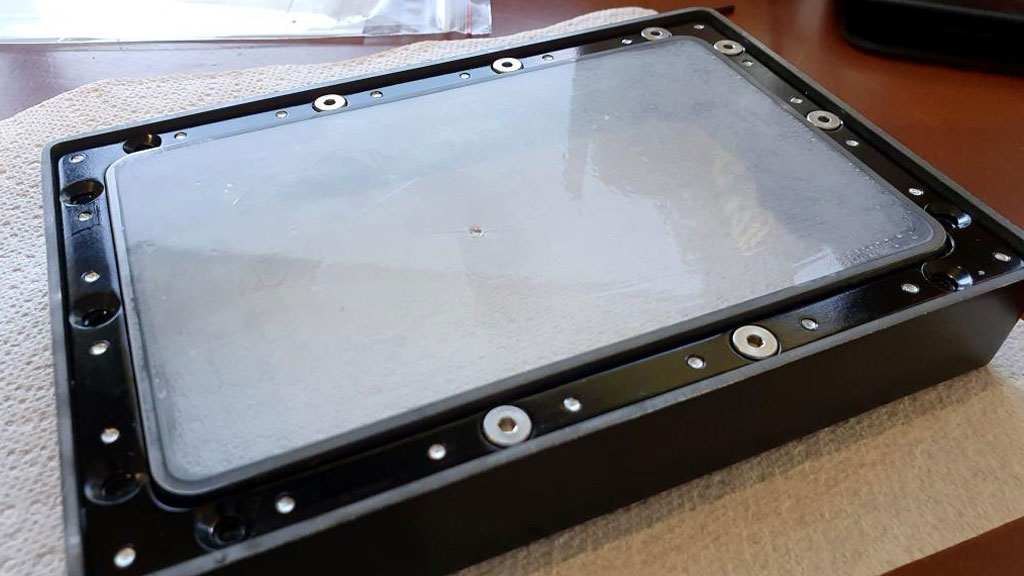

Common FEP Film Thickness Options
0.05 mm (50 microns)
|
|
Best for: Hobbyists printing detailed models, figurines, or parts with delicate features.
0.1 mm (100 microns)
|
|
Best for: General-purpose printing – a versatile option suitable for most resin 3D printer users.
0.15 mm (150 microns)
|
|
Best for: Industrial users or those printing large, less detailed models where longevity matters more than microscopic accuracy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Thickness
1. Printer Size & Type
- Small-format printers benefit from thinner films (0.05–0.1 mm) for precision.
- Large-format printers may need thicker films (0.1–0.15 mm) to handle stress.
2. Model Complexity
- Detailed miniatures → 0.05 mm.
- General models → 0.1 mm.
- Large prototypes → 0.15 mm.
3. Printing Frequency
- Occasional users can prioritize detail with thinner films.
- Heavy users should invest in thicker films for durability.
4. Resin Type
- Flexible resins work better with thinner films (to reduce peel stress).
- Standard or tough resins pair well with thicker films.
Conclusion
There’s no universal answer – the best FEP film thickness depends on your printer setup and project type:
- 0.05 mm: For maximum detail and precision.
- 0.1 mm: The best all-rounder, balancing durability and print quality.
- 0.15 mm: For longevity and large prints with less focus on fine detail.
If you’re new to resin printing, starting with 0.1 mm is often the safest choice. As you gain experience, experimenting with thinner or thicker FEP films will help you fine-tune your setup to match your 3D printing goals.