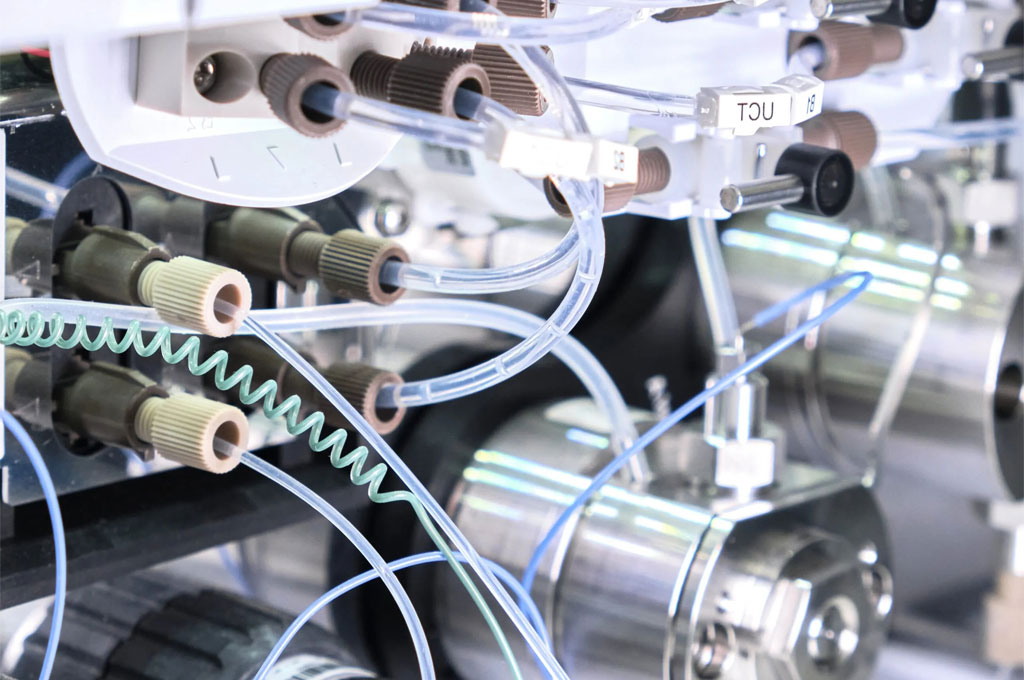
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) capillary tubing has become a vital component in modern chromatography systems due to its exceptional chemical resistance, low surface energy, and smooth internal bore.
Whether dealing with aggressive solvents, delicate biomolecules, or high-purity requirements, PTFE capillary tubing offers the inertness and durability necessary to maintain system integrity and accuracy.
Its versatility makes it suitable for multiple chromatography techniques, each with distinct operational demands.
1. HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography)
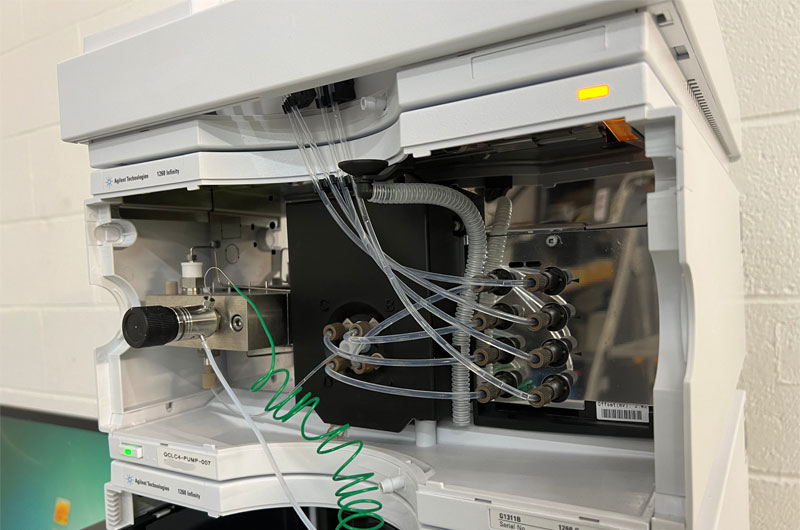

In HPLC, the purity and reliability of solvent transfer lines directly influence analytical accuracy.
PTFE capillary tubing is ideal for transporting solvents from reservoirs to the pump and from the injector to the column because it resists chemical attack from a broad range of mobile phases, including strong acids, bases, and organic solvents. Its ultra-smooth inner surface minimizes adsorption of analytes, reducing carryover and improving reproducibility.
In sample injection pathways, PTFE tubing ensures that delicate analytes pass through without chemical interaction, helping maintain precise retention times and consistent chromatographic profiles.
2. Gas Chromatography (GC)
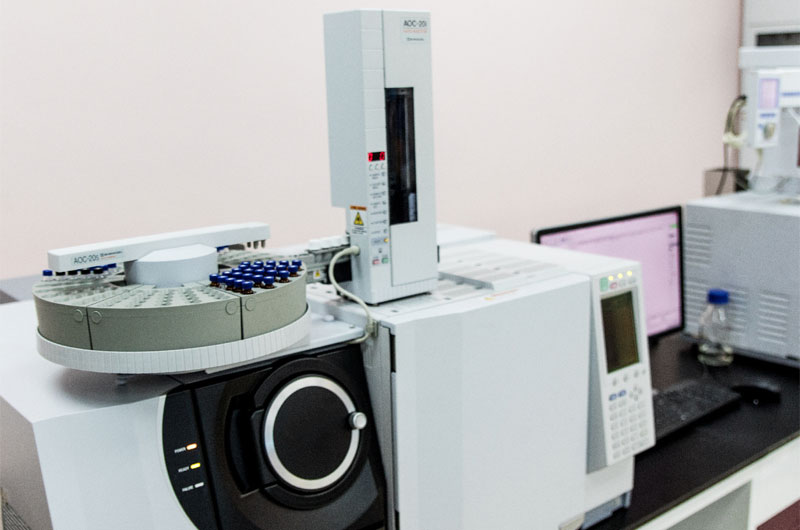

In GC, carrier gases such as helium, nitrogen, or hydrogen must travel through tubing without contamination or adsorption.
PTFE capillary tubing’s low gas permeability and inertness prevent sample degradation or interference. Its flexibility and resistance to temperature fluctuations make it a reliable choice for connecting injection ports, detectors, and other system components.
When used for sample introduction, PTFE ensures that volatile compounds retain their integrity during transit, improving sensitivity and resolution in analytical results.
3. Ion Chromatography (IC)
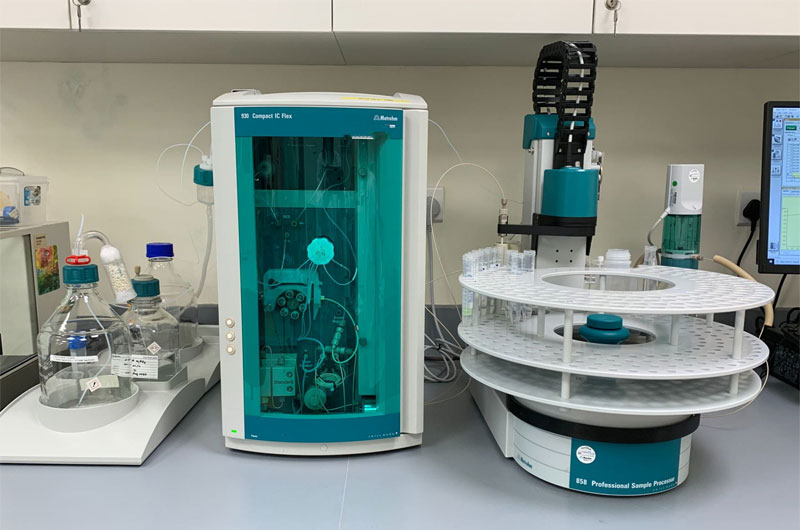

Ion chromatography often deals with high-purity water, buffered solutions, and ionic species that are highly sensitive to contamination.
PTFE’s non-reactive nature ensures that no metallic ions or extractables leach into the sample stream. Its smooth bore minimizes ion adsorption, which is critical for maintaining peak shape and quantification accuracy.
In IC systems, PTFE tubing is often used in pump inlet lines, eluent delivery, and detector connections, where purity is paramount to achieving accurate ionic separation and quantification.
4. Preparative Chromatography
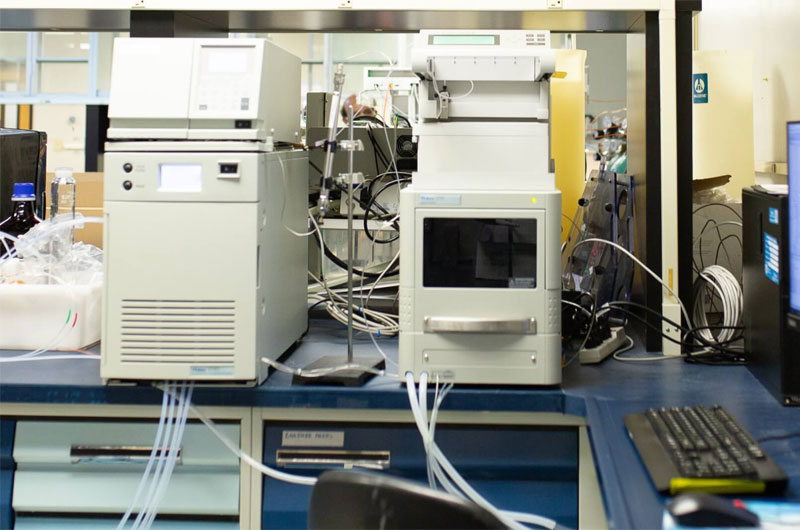

Preparative chromatography operates on a larger scale, often involving higher flow rates, stronger solvents, and higher concentrations of target compounds.
PTFE tubing’s robustness and chemical resistance make it suitable for solvent transfer, column connections, and fraction collection systems. Since preparative work often involves recovering valuable compounds, PTFE’s low adsorption properties help maximize yield and prevent loss of target molecules to tubing surfaces.
Its compatibility with both aqueous and organic phases ensures reliable performance across diverse separation processes.
5. Biochromatography
Biochromatography requires gentle handling of fragile biomolecules like proteins, antibodies, and nucleic acids.
PTFE capillary tubing provides an inert, low-friction pathway that reduces shear forces and minimizes protein denaturation or adsorption. Its biocompatibility and resistance to biofouling make it an excellent choice for sample delivery, column connections, and detector interfaces in bioseparation systems.
Additionally, PTFE’s non-stick properties help prevent blockages and make cleaning easier, which is particularly valuable in systems requiring frequent changeovers.