One of the most common forms in which PTFE is supplied is in bar shapes, including round, square, and rectangular bars.
In this article, we’ll explore the various PTFE bar shapes—round, square, and rectangular, discussing their characteristics, typical applications, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
1. PTFE Round Bars
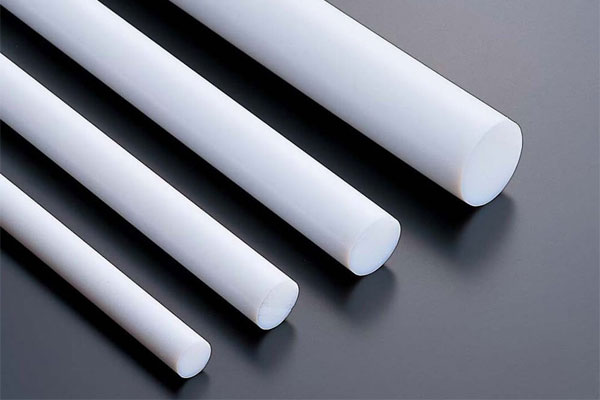

PTFE round bars are cylindrical in shape and are the most commonly used PTFE bar form. They are manufactured by extrusion or compression molding followed by sintering. PTFE round bars are available in a wide range of diameters and lengths, offering great flexibility for machining and further processing.
Key Characteristics:
- Smooth surface finish
- Excellent machinability
- Uniform diameter and structure
- High dimensional stability
- Resistant to chemicals, heat, and wear
Common Applications
PTFE round bars are ideal for producing components that require rotational symmetry or need to fit into cylindrical assemblies. Typical applications include:
- Bushings
- Seals and gaskets
- Rollers
- Insulation spacers
- Valve seats
- Rod guides
These components often demand low friction and high wear resistance, making PTFE round bars a perfect choice.
2. PTFE Square Bars
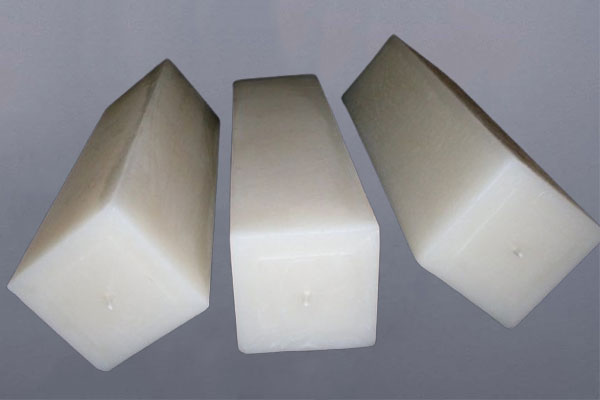

PTFE square bars are shaped with equal width and height across the cross-section, forming a perfect square. Like round bars, they are produced through molding or extrusion and are available in various sizes.
Key Characteristics:
- Flat surfaces on all sides
- Easy to clamp and hold for machining
- Useful for applications needing straight, edge-to-edge contact
- Excellent dielectric and chemical resistance
Square bars offer a stable profile that makes them suitable for structural and support components in equipment and fixtures.
Common Applications
PTFE square bars are often used in applications where a flat, even surface is required or where the bar will be secured in place without rotation. Common uses include:
- Structural support in corrosion-prone environments
- Spacer blocks
- Wear strips
- Sliding bearings
- Electrical insulation panels
Their geometry allows for even distribution of load and ease of stacking, which can be advantageous in mechanical assemblies.
3. PTFE Rectangular Bars
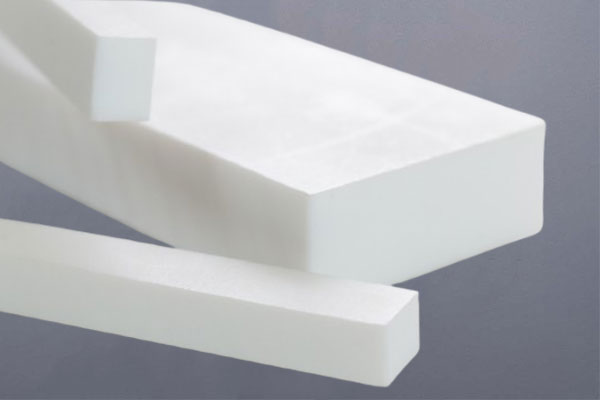

PTFE rectangular bars (also referred to as flat bars) have a rectangular cross-section with different width and height dimensions. They are particularly useful where a flatter profile is required and are typically manufactured via compression molding.
Key Characteristics:
- Wide, flat surfaces
- Can be easily machined into sheets, strips, or custom parts
- Greater surface area for contact and mounting
- Ideal for sliding or wear applications
Due to their geometry, rectangular bars can provide more surface contact and coverage than round or square bars, making them suitable for large-area protection or movement.
Common Applications
PTFE rectangular bars are widely used in applications requiring a flat, non-stick surface or where low-friction movement is necessary across a large area. These include:
- Scraper blades
- Wear plates
- Slide pads
- Conveyor system liners
- Thermal and electrical insulation barriers
Their shape allows them to be used both as standalone parts or as raw materials for CNC machining into complex components.
4. Comparative Overview of Round, Square, and Rectangular PTFE Bars
| Feature | Round Bar | Square Bar | Rectangular Bar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Cylindrical | Equal-sided square | Flat with unequal sides |
| Machinability | High | Moderate to high | High |
| Common Applications | Bearings, seals, spacers | Structural blocks, sliders | Wear plates, scrapers, guides |
| Surface Area Contact | Minimal | Moderate | Large |
| Load Distribution | Radial symmetry | Even on four sides | Even across large flat surfaces |
| Storage/Handling | Rolls/rods | Stackable cubes | Stackable flat slabs |
5. How to Choose the Right PTFE Bar Shape
When selecting a PTFE bar shape for your application, consider the following factors:
1. Application Requirements
- Dynamic Parts: Round bars are best for rotating parts like bushings and seals.
- Structural or Stationary Parts: Square and rectangular bars are better suited for static support structures.
- Sliding Components: Rectangular bars provide the needed surface area for wear and low-friction movement.
2. Machining Capabilities
Evaluate the equipment available in your workshop or facility. Round bars are easier to mount on lathes, while rectangular bars are ideal for milling operations.
3. Assembly and Fit
Match the bar shape with the component design:
- Use round bars for insertion into circular bores.
- Use square/rectangular bars for components that require precise edge alignments.
4. Cost and Availability
PTFE round bars are more commonly produced and readily available in various sizes, often making them more cost-effective. Rectangular and square bars, while available, may have fewer standard size options and require custom production.