6 Common FEP Film Problems in 3D Printing and How to Fix Them
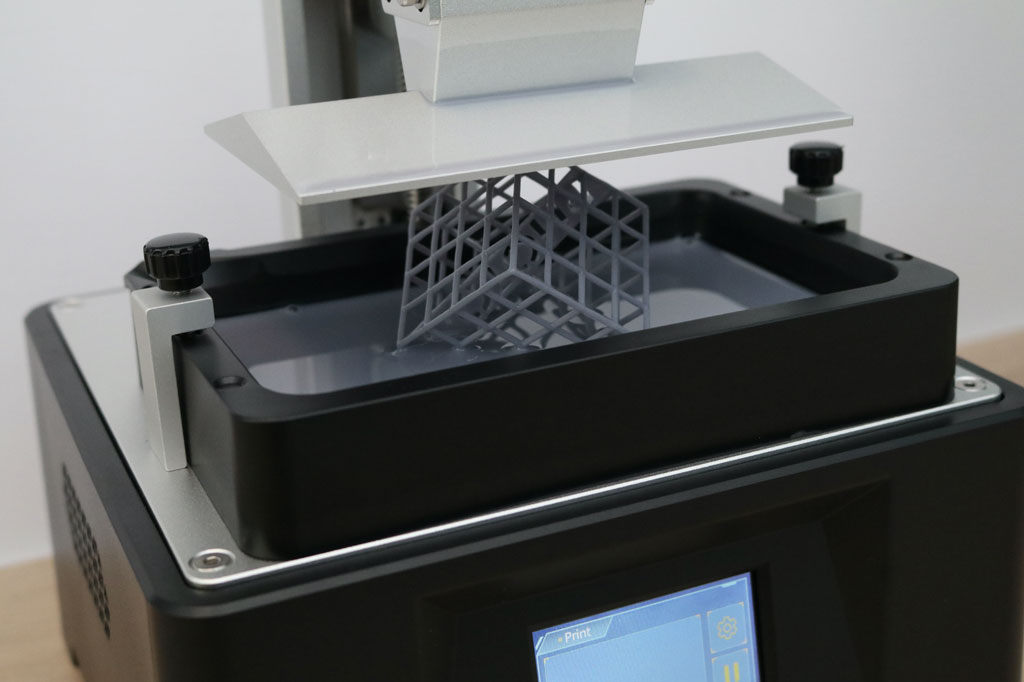
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) film plays a crucial role in resin-based 3D printing, particularly in SLA (Stereolithography) and MSLA (Masked Stereolithography) printers. It acts as a non-stick layer between the cured resin and the bottom of the resin vat, allowing prints to release cleanly. Despite its critical function, FEP film can develop issues over time, […]
6 Common FEP Film Problems in 3D Printing and How to Fix Them Read More »